The challenge: Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
More than 55 million people worldwide have been diagnosed with dementia and the number is only expected to increase by 10 million every year due to the world’s ageing population1. One of the main problems patients and physicians face is the fact that dementia currently has no cure so the treatment options available are, as of now, primarily focused on mitigating the symptoms of those affected by dementia and to improve their quality of life2. For that, early diagnosis is key and highly beneficial.
AI and Alzheimer’s Disease
We believe AI can support the clinical pathway of AD and also become important in the post-diagnostic support of patients. Research has shown that AI can be applied to different steps of said clinical pathway, some of the most researched being diagnosis, prognosis and treatment options3.
When it comes to diagnosis, research first focused on neuroimaging in an effort to extract as much information as possible from the brain scans in order to track volume changes and, therefore, brain atrophy4,5. Apart from that, there’s also been research applying AI to cognitive tests6 and speech assessments7, for example.
Quantib® ND, an AI powered tool for brain atrophy quantification and WMH detection
Quantib® ND is an AI software for atrophy quantification from MRI reading designed and developed by Quantib. The AI software is FDA cleared and CE marked (Class IIb) thus complying with the European MDR 2017/745, and therefore, deemed suitable and safe for its use in the clinical setting.
Quantib® ND features include fully automatic brain segmentations and volumetry measurements including total brain volume, ICV and brain structures. Additionally, the software also includes automatic WMH segmentations, yielding the total WMH count and volume, that can be corrected if needed.
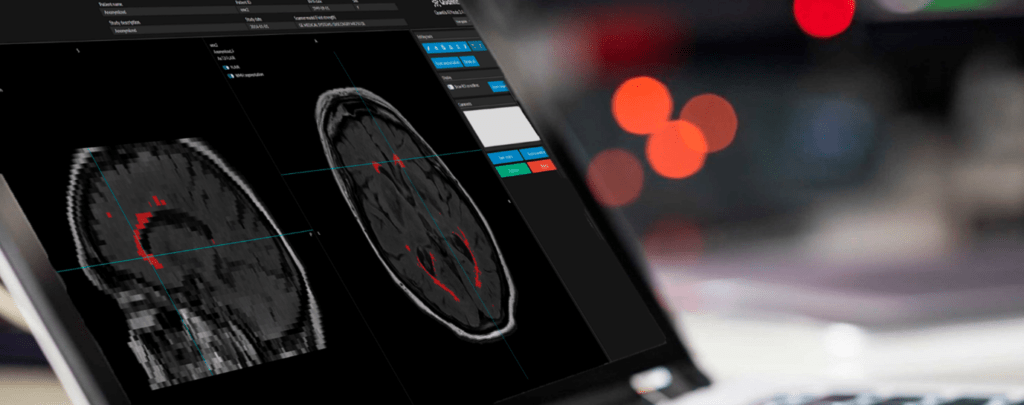
Single-time-point and longitudinal analyses are available to support single examinations as well as follow up exams and WMH progression tracking.
The software provides different outputs:
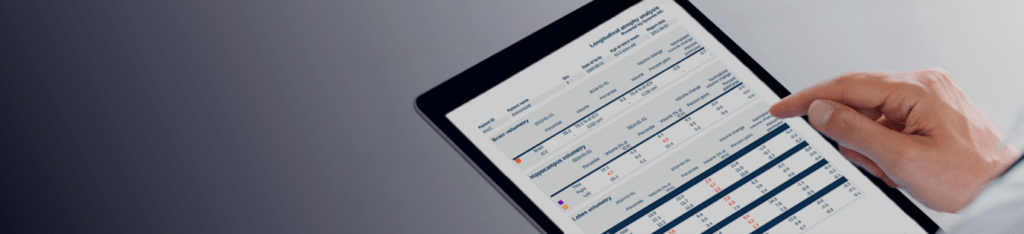
- A complete and standardized report per workflow that includes:
- For brain atrophy analysis:
- Tables that depict the brain, hippocampus and brain lobes volumetry, volumetry change and percentiles.
- Reference centile curves for brain, lobes, cerebellum and hippocampus volumes that allow the comparison of patient brain volume development to the mean values for a non-demented population. These reference curves contain valid data for patients aged 45 to 95 and are based on data acquired in the Rotterdam Scan Study8.
- For WMH analysis:
- Total amount and volume of pre-existing, disappearing and new hyperintensities.
- Overview images.
- For brain atrophy analysis:
- Brain segmentations are exported as DICOM series.
Clinical use of Quantib® ND
Currently, there are multiple published and on-going scientific studies that explore the use and the value of Quantib® ND in clinical settings.
Facebook Twitter LinkedIn WhatsApp Condividi
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Dementia Observatory (GDO). https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/global-dementia-observatory-gdo (2021).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Dementia. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (2021).
- Fabrizio, C., Termine, A., Caltagirone, C. & Sancesario, G. Artificial Intelligence for Alzheimer’s Disease: Promise or Challenge? Diagnostics 11, 1473 (2021).
- Qiu, S. et al. Multimodal deep learning for Alzheimer’s disease dementia assessment. Nat Commun 13, 3404 (2022).
- Brierley, C. AI could detect dementia years before symptoms appear. University of Cambridge (2021).
- Li, R. et al. Applications of artificial intelligence to aid early detection of dementia: A scoping review on current capabilities and future directions. J Biomed Inform 127, 104030 (2022).
- Fristed, E. et al. Evaluation of a speech-based AI system for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease remotely via smartphones. doi:10.1101/2021.10.19.21264878.
- Ikram, M. A. et al. The Rotterdam Scan Study: design update 2016 and main findings. J. Epidemiol. 30, 1299–315 (2015).
Site: www.quantib.com
